Liver Cancer
The liver is the largest organ in the body. It is found behind the ribs on the right side of the abdomen. The liver has two parts, a right lobe and a smaller left lobe.
The liver has many important functions that keep a person healthy. It removes harmful material from the blood. It makes enzymes and bile that help digest food. It also converts food into substances needed for life and growth.
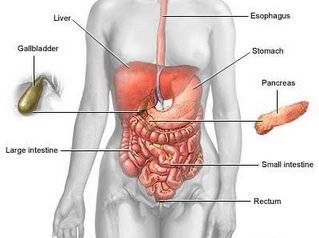
The liver gets its supply of blood from two vessels. Most of its blood comes from the hepatic portal vein. The rest comes from the hepatic artery.
Most primary liver cancers begin in hepatocytes (liver cells). This type of cancer is called hepatocellularcarcinoma or malignant hepatoma. Children may develop childhood hepatocellular carcinoma or hepatoblastoma. This information does not deal with childhood liver cancer.
When liver cancer spreads (metastaseses) outside the liver, the cancer cells tend to spread to nearby lymph nodes and to the bones and lungs. When this happens, the new tumour has the same kind of abnormal cells as the primary tumour in the liver. For example, if liver cancer spreads to the bones, the cancer cells in the bones are actually liver cancer cells. The disease is metastatic liver cancer, not bone cancer. It is treated as liver cancer, not bone cancer.
Similarly, cancer that spreads to the liver from another part of the body is different from primary liver cancer. The cancer cells in the liver are like the cells in the original tumour. When cancer cells spread to the liver from another organ (such as the colon, lung, or breast), doctors may call the tumour in the liver a secondary tumour.
more...
The liver has many important functions that keep a person healthy. It removes harmful material from the blood. It makes enzymes and bile that help digest food. It also converts food into substances needed for life and growth.

The liver gets its supply of blood from two vessels. Most of its blood comes from the hepatic portal vein. The rest comes from the hepatic artery.
Most primary liver cancers begin in hepatocytes (liver cells). This type of cancer is called hepatocellularcarcinoma or malignant hepatoma. Children may develop childhood hepatocellular carcinoma or hepatoblastoma. This information does not deal with childhood liver cancer.
When liver cancer spreads (metastaseses) outside the liver, the cancer cells tend to spread to nearby lymph nodes and to the bones and lungs. When this happens, the new tumour has the same kind of abnormal cells as the primary tumour in the liver. For example, if liver cancer spreads to the bones, the cancer cells in the bones are actually liver cancer cells. The disease is metastatic liver cancer, not bone cancer. It is treated as liver cancer, not bone cancer.

Similarly, cancer that spreads to the liver from another part of the body is different from primary liver cancer. The cancer cells in the liver are like the cells in the original tumour. When cancer cells spread to the liver from another organ (such as the colon, lung, or breast), doctors may call the tumour in the liver a secondary tumour.


